前言
在React中,通常会使用到多层组件嵌套,有些时候最内层组件可能会需要最外层组件的值,如果嵌套的太深则通过Props进行获取就会变得极其麻烦,并且最外层的值可能在多个子组件中需要使用,而Context 提供了一种在组件之间共享此类值的方式,而不必显式地通过组件树的逐层传递 props。
何时使用Context
Context 设计目的是为了共享那些对于一个组件树而言是“全局”的数据。如下,在Context组件中,嵌套了Toolbar组件,在Toolbar组件中,最后渲染的其实是SonButton组件,如果需要在SonButton组件中使用Context组件中的值,那么则可以通过context进行传值。
- 首先需要创建一个上下文:
const TestContext = React.createContext({defaultType: '', defaultValue: ''});设定所需要的默认字段; - 在Context组件中使用
<TestContext.Provider></TestContext.Provider>提供一个provider,并设置默认值defaultType为button,defaultValue为click me; - 将Toolbar组件嵌套在
<TestContext.Provider></TestContext.Provider>中,则Toolbar以及其内部嵌套的子组件都可以通过定义好的TestContext拿到设置的context值; - 在Toolbar组件中其实相当于又嵌套了SonButton组件,通过
static contextType = TestContext读取当前provider的context,并使用this.context进行获取,contextType是固定的,必须通过该值进行接收; - 另外在SonButton组件中又嵌套了GrandSonButton组件,通过相同的方式获取defaultType与defaultValue,也都可以正常获取,因为它们都在<TestContext.Provider>中;
import React from "react";
function Toolbar() {
return (
<div>
<SonButton/>
</div>
);
}
const TestContext = React.createContext({defaultType: '', defaultValue: ''});
class Context extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {};
}
render() {
return (
<TestContext.Provider value={{defaultType: 'button', defaultValue: 'click me'}}>
<Toolbar />
</TestContext.Provider>
);
}
}
class SonButton extends React.Component {
// 指定 contextType 读取当前的 context。
// React 会往上找到最近的 Provider,然后使用它的值。
// 在这个例子中,当前的 defaultType 值为 “button”,defaultValue值为click me 。
static contextType = TestContext;
render() {
return (
<div>
<GrandSonButton/>
<input type={this.context.defaultType} value={this.context.defaultValue}/>
</div>);
}
}
class GrandSonButton extends React.Component {
// 指定 contextType 读取当前的 context。
// React 会往上找到最近的 Provider,然后使用它的值。
// 在这个例子中,当前的 theme 值为 “dark”。
static contextType = TestContext;
render() {
return <input
type={this.context.defaultType} value={this.context.defaultValue}/>;
}
}
export default Context;
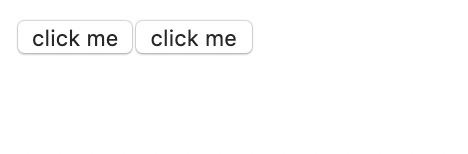
显示结果:
使用Context之前的考虑
Context 主要应用场景在于很多不同层级的组件需要访问同样一些的数据,但是应用context也会使得组件的复用性降低,Context 能让你将这些数据向组件树下所有的组件进行“广播”,所有的组件都能访问到这些数据,也能访问到后续的数据更新。使用 context 的通用的场景包括管理当前的 locale,theme,或者一些缓存数据,这比替代方案要简单的多。
Context API
- React.createContext:创建一个context对象
如const MyContext = React.createContext(defaultValue); 创建了一个名称为MyContext的context对抗,当 React 渲染一个订阅了这个 Context 对象的组件,这个组件会从组件树中离自身最近的那个匹配的 Provider 中读取到当前的 context 值;只有当组件所处的树中没有匹配到 Provider 时,其 defaultValue 参数才会生效,将 undefined 传递给 Provider 时,消费组件的 defaultValue 不会生效,即如上述例子中在Context组件直接使用Toolbar组件,而不是嵌套在Provider中。
class Context extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {};
}
render() {
return (
<Toolbar />
// <TestContext.Provider value={{defaultType: '', defaultValue: ''}}>
//
// </TestContext.Provider>
);
}
}

-
Context.Provider:提供一个Provider
每个 Context 对象都会返回一个 Provider React 组件,它允许消费组件订阅 context 的变化。如上述例子中定义了一个名称为MyContext的Provider,Provider 接收一个 value 属性,传递给消费组件。一个 Provider 可以和多个消费组件有对应关系。多个 Provider 也可以嵌套使用,如果属性名称相同则里层的会覆盖外层的数据。当 Provider 的 value 值发生变化时,它内部的所有消费组件都会重新渲染。Provider 及其内部 consumer 组件都不受制于 shouldComponentUpdate 函数,因此当 consumer 组件在其祖先组件退出更新的情况下也能更新。 -
Class.contextType:获取context
挂载在 class 上的 contextType 属性会被重赋值为一个由 React.createContext() 创建的 Context 对象。这能让你使用 this.context 来消费最近 Context 上的那个值。你可以在任何生命周期中访问到它,包括 render 函数中。contextType可以在class内部使用(static contextType = TestContext),也可以在class外部使用(Context.contextType = TestContext),这只不过是因为ES6的原因导致写法不同而已。 -
Context.Consumer:函数式组件中使用
通过使用Context.Consumer能够在函数式组件中订阅到context,使用需要将要使用的context值作为Context.Consumer的子元素,并且在内部通过函数的形式返回一个React节点,传递给函数的 value 值等同于往上组件树离这个 context 最近的 Provider 提供的 value 值。如果没有对应的 Provider,value 参数等同于传递给 createContext() 的 defaultValue。
class SonButton extends React.Component {
// 指定 contextType 读取当前的 context。
// React 会往上找到最近的 Provider,然后使用它的值。
// 在这个例子中,当前的 theme 值为 “dark”。
static contextType = TestContext;
render() {
return (
<div>
<GrandSonButton/>
<input type={this.context.defaultType} value={this.context.defaultValue}/>
</div>);
}
}
// 函数式组件值中使用TestContext.Consumer
function GrandSonButton() {
return (
<div>
<TestContext.Consumer>
{({defaultType, defaultValue}) => (
// 函数内部也还可以继续使用 <TestContext.Consumer>,只要保证返回的是React接待即可。
<input type={defaultType} defaultValue={defaultValue}/>
)}
</TestContext.Consumer>
</div>
)
}
GrandSonButton.contextType = TestContext;

- Context使用示例
在Context中不仅可以传递字段,当然也可以传递函数,通过传递函数的方式可以在嵌套在内部的子组件中更新context,同时通过使用多个Provider嵌套可以实现更为复杂的业务逻辑。在下面的例子中,通过在context中设置一个onChangeValue函数,在子组件中去调用,来改变context;如下示例,点击按钮,则按钮中的value值将会变为i has clicked。
const TestContext = React.createContext({defaultType: 'button', defaultValue: 'click', onChangeValue: () => {}});
class Context extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
value: 'click me'
};
}
handleChange = () => {
this.setState({
value: 'i has clicked'
});
};
render() {
return (
<TestContext.Provider value={{defaultType: 'button', defaultValue: this.state.value, onChangeValue: () => {this.handleChange()}}}>
<Toolbar />
</TestContext.Provider>
);
}
}
class SonButton extends React.Component {
static contextType = TestContext;
render() {
return (
<div>
<GrandSonButton/>
<input type={this.context.defaultType} value={this.context.defaultValue} onClick={this.context.onChangeValue}/>
</div>);
}
}
总结
综上,可以看出在使用多层组件嵌套并且多个嵌套的子组件需要接收父组件中传递的值时,因为props需要一层一层获取会显得比较麻烦,使用Context通过Provider的方式,在子组件中可以灵活的获取父组件的属性或者方法,但是这也使得组件的复用性降低,因此在使用的过程中,应该灵活变通,Context与props可以混合使用。